Ai-Assisted Code Generation With Privacy Guarantees: Securely Deploy SantaCoder With BlindBox on Azure
In this article, we'll demonstrate how you can efficiently analyze code at scale while maintaining privacy. We'll use BlindBox, our open-source secure enclave tooling, to serve StarCoder with privacy guarantees on Azure.
With the explosion of Large Language Models like ChatGPT, automated code generation, and analysis has well and truly established its role as a key player in the future of software engineering.
Key Takeaways:
- LLMs for code have multiple use cases, such as improving code quality, increasing productivity, and automating software migration. Different methods exist, from closed-source SaaS solutions that analyze sent code to them to open-source models deployed on-device, like StarCoder from BigCode.
- However, both deployment modes have their own issues: the former is not privacy-friendly as data is exposed to those SaaS providers, and the latter is hard to deploy and maintain for many scenarios.
- In this article, we are going to show you how you can get the best of both worlds and serve LLMs for code analysis at scale with privacy guarantees.
We will provide a concrete example by serving Star Coder using BlindBox, our open-source tooling for confidential app deployments, enabling the serving of AI models in a privacy-preserving way.
Context
Today LLMs are typically deployed using server-side or on-device deployment.
Deploying LLMs on the server side, for instance, on a GPU hosted in a Public Cloud, has several advantages:
- The model can be large and intensive since computation is performed on the AI provider’s server machine, not on users’ devices. One can gather complex hardware stacks with several Nvidia A100s, for instance, to run complex models at scale and add complex orchestration to have all code from an organization pre-indexed to leverage it for code analysis.
- This method provides ease of use for the end user since the AI provider will handle the configuration and maintenance of their service. APIs can be served with quick onboarding and no setup cost for end users.
However, there is a significant flaw in this remote deployment model: there are no guarantees that the code sent to these models will remain confidential and private.
When an engineer sends proprietary code to a SaaS provider with an LLM to help developers, this code could be accessible in clear to some employees.
Indeed, even if data can be protected at rest and transit through encryption, data is still decrypted in memory as it needs to be processed. But because this last mile is not covered, data owners have no guarantee over what happens on the code they send as it could be copied, redistributed, leaked, etc., by mistake, intentionally, or due to a compromise.
This leads to a too-high risk for some clients with confidential data and strict compliance requirements, often meaning they must miss out on leveraging these key AI tools.
On-device deployment can solve privacy issues as the code remains on users’ devices. However, this method has two key disadvantages:
- AI models’ storage space and power are limited by user devices. Deploying LLMs on-device or on-premise requires high-spec hardware and expertise.
- Model weights are exposed when deployed on the client side, which can prevent AI providers of models with very sensitive IP from deploying on-device, as they risk their weights being stolen.
With significant disadvantages for both methods, at Mithril Security, we have been focusing our energy on creating a way of serving LLMs that is both easy to use and privacy-friendly.
Privacy-friendly AI serving
Our solution centers around facilitating and securing the deployment of models within privacy-preserving Trusted Execution Environments (TEEs), also sometimes called secure enclaves. TEEs are hardware-based secure environments that can be created using the latest processors from Intel, AMD, and Nvidia.
Those machines are today largely available on all major Cloud providers, such as Azure Confidential Computing.
Deploying models inside TEEs combines the best of both worlds:
- Models are deployed server-side to leverage a state-of-the-art and unified hardware/software stack for maximal performance and little user setup time.
- Code privacy is ensured even though code is sent remotely.
- Model privacy is ensured as the model remains on the server side.
This is achievable using Confidential Computing (CC) technologies, which work by encrypting all memory within its self-contained, isolated environment and blocking attempts to access this memory from outside of the environment.
CC technologies also offer a verification mechanism called attestation. Attestation is configured to be performed by default with BlindBox- no additional actions are required by our users. If any of our attestation checks fail, the end user will be unable to connect to the BlindBox. The attestation process with BlindBox will verify the following elements:
- We are communicating with a genuine AMD SEV-SNP confidential VM.
- We are communicating with a genuine Azure-compliant VM. The VM is running in production mode and not debug mode. By deploying a model within a TEE, AI providers can offer SaaS solutions with all the benefits of server-side deployment while providing privacy guarantees that customers' code is not exposed to them thanks to end-to-end protection.
Example: Deploying SantaCoder with BlindBox
Let’s see how AI models can be served with privacy guarantees using TEEs through BlindBox, our open-source secure enclave tooling. BlindBox adds isolation layers to images (for instance, Docker or Kubernetes) before deploying them on Confidential VMs from a Cloud Provider.
We will show how to deploy SantaCoder, an LLM created by BigCode that provides code generation or fill-in-the-middle code completion, on confidential containers on Azure Container Instances (ACI) to ensure the code sent to the model remains private.
By deploying SantaCoder with BlindBox, any code sent to the model is protected end-to-end. It cannot be accessed by the AI provider, as data is encrypted by a key known only to the data owner. This means the AI provider can guarantee that the code sent to them to be analyzed by their coding assistant is not exposed to any third party.
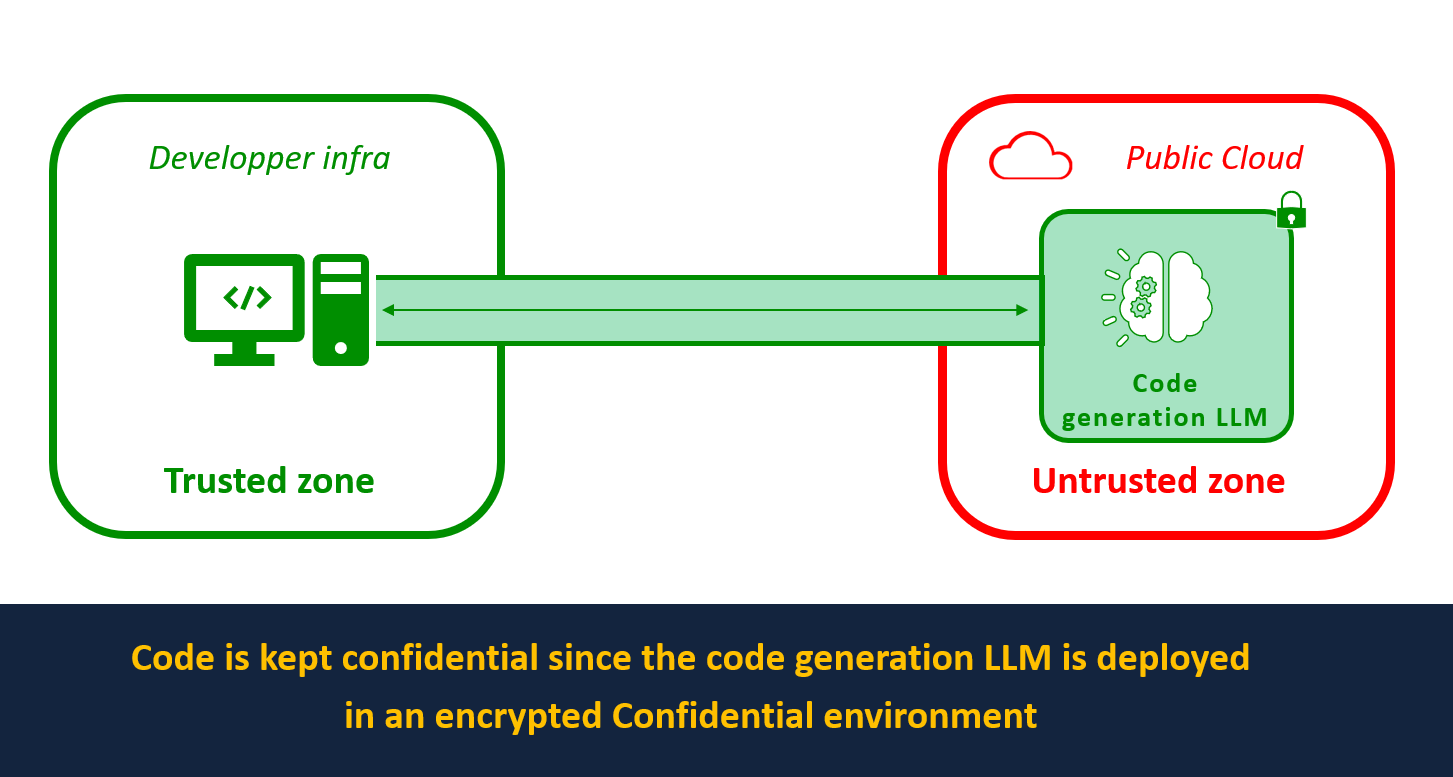
You can see how to deploy SantaCoder on Azure Confidential Computing infrastructure to ensure the privacy of code sent for analysis by following our integration tutorial in our docs.
Conclusion
This article shows how we can greatly reduce privacy exposure when using remotely hosted LLM-fueled coding assistants, thanks to their deployment in TEEs with BlindBox. If you want to learn more about our BlindBox solution and the confidential computing technologies behind it, check out our official documentation page.
If you like our project, please drop a ⭐ on our GitHub, and don't hesitate to reach out to us to learn more!
Want to learn more about Zero-Trust LLM deployment?
Image credits: Edgar Huneau